FireBrick SIP Configuration: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Update deprecated tags |
||
| (35 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:2700-small.png|link=:Category:FireBrick]] |
|||
[[File:Pbvoipicon.png]]Also see: [http://www.firebrick.co.uk/fb2700/voip.php FireBrick VoIP Page] which has more details about the feature. |
|||
=Overview= |
|||
''(This is a first draft and may need updating. - 10 October 2012)'' |
|||
[[File:Pbvoipicon.png]] |
|||
Also see: [https://www.firebrick.co.uk/support/knowledge-base/voip/ FireBrick VoIP Page] which has more details about the feature, as well as the [https://www.firebrick.co.uk/support/manuals/0 FireBrick Manuals] which contain a VoIP section. |
|||
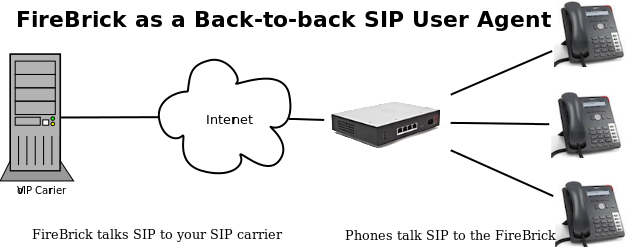
The FireBrick can be used for VoIP by being a VoIP gateway (FBSIP). Your local (or remote) SIP devices register against the FireBrick, and the FireBrick registers to your SIP provider, in a sense the Firebrick acts as a back-to-back SIP gateway. |
The FireBrick can be used for VoIP by being a VoIP gateway (FBSIP). Your local (or remote) SIP devices register against the FireBrick, and the FireBrick registers to your SIP provider, in a sense the Firebrick acts as a back-to-back SIP gateway. |
||
| Line 11: | Line 14: | ||
We'll set this up so that incoming calls route to a 'ring group', which in turn will route to a number of internal extensions. Outgoing calls from the local phones will all go out via the single SIP account with the service provider. |
We'll set this up so that incoming calls route to a 'ring group', which in turn will route to a number of internal extensions. Outgoing calls from the local phones will all go out via the single SIP account with the service provider. |
||
=SIP and NAT= |
==SIP and NAT== |
||
First, a few comments about SIP, NAT and the FireBrick... |
First, a few comments about SIP, NAT and the FireBrick... |
||
The FireBrick maps ports and IPs for NAT but provides no ALG for SIP or any other protocol. SIP is notoriously difficult with any sort of NAT, with or without ALGs. |
The FireBrick maps ports and IPs for NAT but provides no ALG for SIP or any other protocol. SIP is notoriously difficult with any sort of NAT, with or without ALGs. AAISP will be happy to route a block of IP addresses for use with VoIP phones, and the FireBrick can be configured to use these, and even allocate phones from the same manufacturer the correct IP by DHCP. |
||
We have seen SIP work with FireBricks in this case, where the end device and the SIP call server both do things in just the right strange and non standard way to cope with the mapping, but it is rare. It also usually requires that UDP sessions be configured to be open for a long time on the FireBrick (ongoing-timeout setting on the firewall rules). |
We have seen SIP work with FireBricks in this case, where the end device and the SIP call server both do things in just the right strange and non standard way to cope with the mapping, but it is rare. It also usually requires that UDP sessions be configured to be open for a long time on the FireBrick (ongoing-timeout setting on the firewall rules). |
||
| Line 22: | Line 26: | ||
Having said this, the a FireBrick acting as a SIP server that itself is not behind NAT will try to cope with SIP clients that are behind NAT. This means that in many cases if there are SIP phones behind NAT than they may well work when registering against the FireBrick. |
Having said this, the a FireBrick acting as a SIP server that itself is not behind NAT will try to cope with SIP clients that are behind NAT. This means that in many cases if there are SIP phones behind NAT than they may well work when registering against the FireBrick. |
||
[[File:FBVoIPDia.png|border]] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
The FireBrick has built in configuration to give priority to small packets. This would include RTP as well as DNS, SSH and other real time protocols that send small packets. |
The FireBrick has built in configuration to give priority to small packets. This would include RTP as well as DNS, SSH and other real time protocols that send small packets. |
||
Normally there is no need to add any extra shaping to improve VoIP through a FireBrick. |
Normally there is no need to add any extra shaping to improve VoIP through a FireBrick. |
||
= |
= Seting-up SIP on the FireBrick = |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
== Add a carrier == |
== Add a carrier == |
||
[[File:FireBrick-VoIP-AA2.png|thumb|Carrier Screenshot]] |
|||
This is the SIP service that you're connecting to: |
This is the SIP service that you're connecting to: |
||
{| border="1" cellpadding="1" cellspacing="1" |
{| border="1" cellpadding="1" cellspacing="1" class="wikitable" |
||
| ⚫ | |||
! Config Item |
|||
! Value |
|||
! Description |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| name |
| name |
||
| |
| AAISP |
||
| Just a name for this particular carrier account |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| Comment |
| Comment |
||
| Main Office Number |
| Main Office Number |
||
| Just for your information |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| username |
| username |
||
| +441234567890 |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
SIP account name ( |
| Your SIP account name as supplied by your carrier (With AAISP, it's the phone number) |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| password |
| password |
||
| **** |
|||
| SIP account password |
| Your SIP account password with the carrier |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| registrar |
| registrar |
||
| voiceless.aa.net.uk |
|||
| SIP Registrar server: registrar.aasip.co.uk |
|||
| The SIP Registrar server, supplied by the carrier |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| proxy |
| proxy |
||
| |
|||
| SIP Proxy server, proxy.aasip.co.uk |
|||
| Not normally needed if using AAISP |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| extn |
| extn |
||
| 100 |
|||
| Internal extension number to call for incoming calls, 100 |
|||
| Internal extension number '''where incoming calls are routed to (e.g. a user or a group)''' |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| allow |
| allow |
||
| |
| 81.187.30.110-119 |
||
| IPs that are allowed to talk SIP to us (i.e. the carriers IPs). (Optional) |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| display-name |
| display-name |
||
| |
| Office |
||
| The Name shown on the phones for incoming calls |
|||
|} |
|} |
||
Click Save. |
Click Save. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang=xml> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
</syntaxhighlight> |
|||
If you go to Status - VoIP, you should see the Carrier listed with an expiry - this shows that the FireBrick is registered to the server. |
If you go to Status - VoIP, you should see the Carrier listed with an expiry - this shows that the FireBrick is registered to the server. |
||
| Line 75: | Line 93: | ||
If you have further SIP accounts with carriers then add those too. |
If you have further SIP accounts with carriers then add those too. |
||
==Next create some users |
==Next create some users== |
||
[[File:FireBrick-VoIP-AA3.png|thumb|VoIP User Screenshot]] |
|||
These will be your local SIP user accounts that your telephones use to register against the FireBrick with. |
These will be your local SIP user accounts that your telephones use to register against the FireBrick with. |
||
Go to: Config - Edit - Setup - Edit VoIP config |
Go to: Config - Edit - Setup - Edit VoIP config |
||
Add new VoIP user: |
Add new VoIP user: |
||
{| border="1" cellpadding="1" cellspacing="1" |
{| border="1" cellpadding="1" cellspacing="1" class="wikitable" |
||
|- |
|||
! Config Item |
|||
! Value |
|||
! Description |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| name |
| name |
||
| John |
| John |
||
| The name for this user |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| display-name |
| display-name |
||
| John |
| John |
||
| Displayed a part of the CLI |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| username |
| username |
||
| john |
| john |
||
| The SIP account username that the phone will use |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| password |
| password |
||
| ******* |
| ******* |
||
| The SIP account password that the phone will use |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| allow |
| allow |
||
| x.x.x.x/24 |
|||
| IPs that are allowed to register, put in your LAN ip addresses, |
| IPs that are allowed to register, put in your LAN ip addresses, e.g., |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| ddi |
| ddi |
||
| +441234567890 |
|||
| The full number for this user, |
| The full number for this user, i.e. same as the carrier's number assigned to you. |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| extn |
| extn |
||
| 101 |
|||
| John's internal extension number, |
| John's internal extension number, can be anything really |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| carrier |
| carrier |
||
| AAISP |
|||
| |
| This will be the carrier John uses to dial out on |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| max-calls |
| max-calls |
||
| 1 |
|||
| |
| If you just want to make 1 call at a time with this account (Optional) |
||
|} |
|} |
||
| Line 113: | Line 146: | ||
xml: |
xml: |
||
<syntaxhighlight lang=xml> |
|||
<telephone name="John" display-name="John" username="john" password="secret" allow="192.168.1.0/24" ddi="+441234567890" extn="101" carrier=" |
<telephone name="John" display-name="John" username="john" password="secret" allow="192.168.1.0/24" ddi="+441234567890" extn="101" carrier="AAISP" max-calls="1"/> |
||
</syntaxhighlight> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
At this point you can configure your SIP phones to register to the FireBrick with the credentials you've specified above. |
At this point you can configure your SIP phones to register to the FireBrick with the credentials you've specified above. |
||
You can then test by calling each other using the extn numbers assigned. |
You can then test by calling each other using the extn numbers assigned. |
||
| Line 124: | Line 158: | ||
==Create a Ring Group== |
==Create a Ring Group== |
||
Ring groups are optional, and allow multiple extensions to be called at once. Here we will create our ring group for incoming calls so that our main number rings all our phones. |
|||
Go to: Config - Edit - Setup - Edit VoIP config |
Go to: Config - Edit - Setup - Edit VoIP config |
||
Click Add New |
Click Add New |
||
{| border="1" cellpadding="1" cellspacing="1" |
{| border="1" cellpadding="1" cellspacing="1" class="wikitable" |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| name |
| name |
||
| Main |
| Main |
||
| Just a name for this group |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| display-name |
| display-name |
||
| Main |
|||
| The name that will display on the phone, |
| The name that will display on the phone, e.g. |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| extn |
| extn |
||
| 100 |
|||
| |
| This is the extension number for this group, used in the Carrier section above |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| ddi |
| ddi |
||
| |
|||
| the telephone number. |
| the telephone number. |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| ring |
| ring |
||
| 101 102 103 |
|||
| space |
| space separated list of the internal extension numbers to ring |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| type |
| type |
||
| Ring All |
|||
| This is the ring type, |
| This is the ring type, e.g. to ring all at once etc. |
||
|} |
|} |
||
Click save. |
Click save. |
||
xml: |
xml: |
||
<syntaxhighlight lang=xml> |
|||
<group name="Main" display-name="Main" extn="100" ddi="+441234567890" ring="101 102 103" type="all"/> |
<group name="Main" display-name="Main" extn="100" ddi="+441234567890" ring="101 102 103" type="all"/> |
||
</syntaxhighlight> |
|||
==Firewall== |
==Firewall== |
||
You will need to open the firewall if you are actually fire-walling traffic to the FireBrick - often people just firewall traffic to the LAN, and therefore all traffic to the FireBrick is allowed. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
SIP and RTP traffic will need to be allowed into the FireBrick. This will need to be from the carrier, but also from external SIP phones if you have any. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
[[Category:FireBrick]] |
[[Category:FireBrick VoIP]] |
||
[[Category:VoIP]] |
[[Category:VoIP]] |
||
Latest revision as of 11:12, 18 May 2022
Overview
Also see: FireBrick VoIP Page which has more details about the feature, as well as the FireBrick Manuals which contain a VoIP section.
The FireBrick can be used for VoIP by being a VoIP gateway (FBSIP). Your local (or remote) SIP devices register against the FireBrick, and the FireBrick registers to your SIP provider, in a sense the Firebrick acts as a back-to-back SIP gateway.
You can have multiple SIP provider (carrier) accounts, and incoming calls can be routed to internal extensions and these extensions can be individual phones or a group which can then ring multiple phones in various ways. An advantage of using the FireBrick in this way is where you are forced to use RFC1918 IP addresses (private) on your LAN and the FireBrick is NATing traffic. Typically the FireBrick will be connected to the ISP by PPP itself and will have a public IP address, therefore the SIP is not being put through NAT. (SIP and NAT don't work well together)
Taking an example of a single SIP account with AAISP, and a couple of SIP phones, a FireBrick can be configured as follows.
We'll set this up so that incoming calls route to a 'ring group', which in turn will route to a number of internal extensions. Outgoing calls from the local phones will all go out via the single SIP account with the service provider.
SIP and NAT
First, a few comments about SIP, NAT and the FireBrick...
The FireBrick maps ports and IPs for NAT but provides no ALG for SIP or any other protocol. SIP is notoriously difficult with any sort of NAT, with or without ALGs. AAISP will be happy to route a block of IP addresses for use with VoIP phones, and the FireBrick can be configured to use these, and even allocate phones from the same manufacturer the correct IP by DHCP.
We have seen SIP work with FireBricks in this case, where the end device and the SIP call server both do things in just the right strange and non standard way to cope with the mapping, but it is rare. It also usually requires that UDP sessions be configured to be open for a long time on the FireBrick (ongoing-timeout setting on the firewall rules).
In general we would never suggest using SIP with NAT for this reason, and it is partly why the FireBrick itself includes a full back to back SIP gateway allowing SIP registrations in and out and a-law RTP via the FireBrick. Used in this way it can avoid any NAT issues, but does specifically need configuring to meet your needs.
Having said this, the a FireBrick acting as a SIP server that itself is not behind NAT will try to cope with SIP clients that are behind NAT. This means that in many cases if there are SIP phones behind NAT than they may well work when registering against the FireBrick.
Prioritising VoIP Traffic
The FireBrick has built in configuration to give priority to small packets. This would include RTP as well as DNS, SSH and other real time protocols that send small packets.
Normally there is no need to add any extra shaping to improve VoIP through a FireBrick.
Seting-up SIP on the FireBrick
![]() Go to Config - Edit - Setup - Edit VoIP config.
Go to Config - Edit - Setup - Edit VoIP config.
Add a carrier
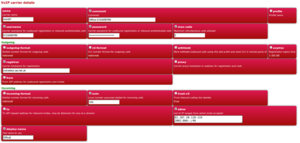
This is the SIP service that you're connecting to:
| Config Item | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| name | AAISP | Just a name for this particular carrier account |
| Comment | Main Office Number | Just for your information |
| username | +441234567890 | Your SIP account name as supplied by your carrier (With AAISP, it's the phone number) |
| password | **** | Your SIP account password with the carrier |
| registrar | voiceless.aa.net.uk | The SIP Registrar server, supplied by the carrier |
| proxy | Not normally needed if using AAISP | |
| extn | 100 | Internal extension number where incoming calls are routed to (e.g. a user or a group) |
| allow | 81.187.30.110-119 | IPs that are allowed to talk SIP to us (i.e. the carriers IPs). (Optional) |
| display-name | Office | The Name shown on the phones for incoming calls |
Click Save.
xml:
<carrier name="AAISP" display-name="Main" allow="81.187.30.110-119" registrar="voiceless.aa.net.uk"username="01234567890" password="secret" extn="100" comment="Main Office Number"/>
If you go to Status - VoIP, you should see the Carrier listed with an expiry - this shows that the FireBrick is registered to the server.
If you have further SIP accounts with carriers then add those too.
Next create some users
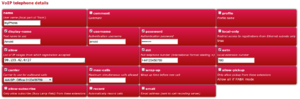
These will be your local SIP user accounts that your telephones use to register against the FireBrick with. Go to: Config - Edit - Setup - Edit VoIP config Add new VoIP user:
| Config Item | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| name | John | The name for this user |
| display-name | John | Displayed a part of the CLI |
| username | john | The SIP account username that the phone will use |
| password | ******* | The SIP account password that the phone will use |
| allow | x.x.x.x/24 | IPs that are allowed to register, put in your LAN ip addresses, e.g., |
| ddi | +441234567890 | The full number for this user, i.e. same as the carrier's number assigned to you. |
| extn | 101 | John's internal extension number, can be anything really |
| carrier | AAISP | This will be the carrier John uses to dial out on |
| max-calls | 1 | If you just want to make 1 call at a time with this account (Optional) |
Click save.
xml:
<telephone name="John" display-name="John" username="john" password="secret" allow="192.168.1.0/24" ddi="+441234567890" extn="101" carrier="AAISP" max-calls="1"/>
You can repeat this process for your other users, changing the extn each time, e.g. 102, 103 etc. At this point you can configure your SIP phones to register to the FireBrick with the credentials you've specified above. You can then test by calling each other using the extn numbers assigned. You will also be able to dial out. If you go to Status - VoIP, you should see the Telephones listed with an expiry, IP and the SIP user agent details - this shows that the SIP phones have registered to the FireBrick. Incoming calls will not work yet, as the Carrier above is set to send calls to extension 100, which we've not created... yet...
Create a Ring Group
Ring groups are optional, and allow multiple extensions to be called at once. Here we will create our ring group for incoming calls so that our main number rings all our phones.
Go to: Config - Edit - Setup - Edit VoIP config Click Add New
| name | Main | Just a name for this group |
| display-name | Main | The name that will display on the phone, e.g. |
| extn | 100 | This is the extension number for this group, used in the Carrier section above |
| ddi | the telephone number. | |
| ring | 101 102 103 | space separated list of the internal extension numbers to ring |
| type | Ring All | This is the ring type, e.g. to ring all at once etc. |
Click save.
xml:
<group name="Main" display-name="Main" extn="100" ddi="+441234567890" ring="101 102 103" type="all"/>
Firewall
You will need to open the firewall if you are actually fire-walling traffic to the FireBrick - often people just firewall traffic to the LAN, and therefore all traffic to the FireBrick is allowed.
SIP and RTP traffic will need to be allowed into the FireBrick. This will need to be from the carrier, but also from external SIP phones if you have any. Take a look at this wiki page for more info: FireBrick and VoIP Firewall