Router:Ubiquiti EdgeRouter Lite: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (7 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The Ubiquiti EdgeRouter Lite can be used as a router (with a suitable modem) with A&A's services. |
The Ubiquiti EdgeMAX ERLite-3 (EdgeRouter Lite 3) can be used as a router (with a suitable modem) with A&A's services. The router is based on a dual-core MIPS64 processor and runs a Linux distribution called EdgeOS which uses a configuration system forked from Vyatta with a web-based interface on top. |
||
This configuration was tested with a UBNT EdgeRouter Lite running v1.9.1 firmware, and a BT ECI FTTC modem. |
|||
= You'll need = |
= You'll need = |
||
* |
* a PPPoE ADSL or FTTC modem, or a fibre ONT (for FTTP). A&A's supplied modems & routers can be configured into a bridge mode for this. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
As of recent firmware versions (at least since v1.9.7-hotfix.4) you can almost achieve a working configuration just by using the Basic Setup wizard in the router's web interface, but there are currently a couple of extra configuration changes you have to do manually to fix IPv6 support. |
|||
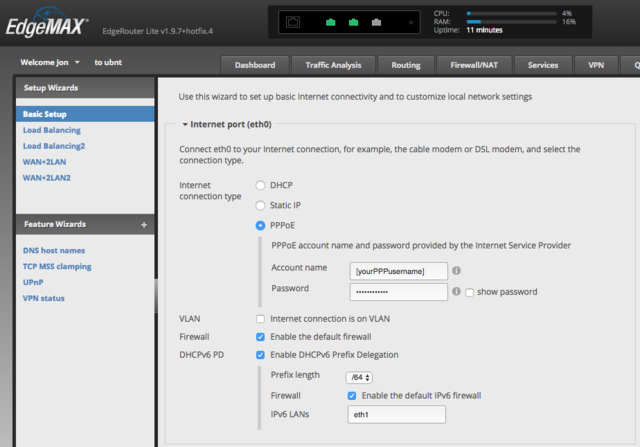
* Connect a computer to the router, access its web interface and start the Basic Setup wizard. Set the 'Internet connection type' option to PPPoE and give it the PPP username and password of your A&A line. Enable the DHCPv6 PD option (which allows for almost entirely automatic configuration of IPv6) and set the IPv6 prefix length that you have set up for your line on the A&A control pages (if you're not sure, it would normally be /64 by default): |
|||
[[File:EdgeOS Basic Setup Wizard.png|640px]] |
|||
* Configure the rest of the Basic Settings Wizard settings however you like or leave them as the defaults. |
|||
* Finish the wizard and reboot. Connect your PPPoE modem to the eth0 port on the router, and your LAN to the eth1 port (to match the conventions used by the setup wizard). You should now have a working IPv4 internet connection. |
|||
* The two things that need to be done to fix IPv6 support are enabling the IPv6 option for the PPPoE connection, and setting up a default route to use the PPPoE interface because an IPv6 route doesn't get added by default when the connection is established. To add those settings enter the router's command-line interface either by using the '''CLI''' button on the web interface or using SSH and then enter the following commands: |
|||
<nowiki>configure |
|||
set interfaces ethernet eth0 pppoe 0 ipv6 enable |
|||
set protocols static interface-route6 ::/0 next-hop-interface pppoe0 |
|||
commit |
|||
save |
|||
exit</nowiki> |
|||
* You don't need to reboot for the changes to take effect and your PPP session should reconnect and come back up with IPv6 configured and working. |
|||
== Other configuration options == |
|||
=== Enabling a 1500 MTU === |
|||
To enable 1500 MTU if you know that your modem can support baby jumbo frames: |
|||
<nowiki>configure |
|||
set interfaces ethernet eth0 pppoe 0 mtu 1500 |
|||
set interfaces ethernet eth0 mtu 1508 |
|||
delete firewall options mss-clamp |
|||
commit |
|||
save |
|||
exit</nowiki> |
|||
=== Enabling UPnP/NAT-PMP/PCP === |
|||
UPnP, NAT-PMP & PCP are protocols that allow devices behind your router to automatically forward ports. |
|||
This can be useful to allow devices such as games consoles to work more easily, but it does have security implications as it allows programs to open holes in your firewall. |
|||
To enable the [https://community.ubnt.com/t5/EdgeMAX/UPnP-vs-UPnP2-What-s-the-difference-between-upnp-and-upnp2/td-p/1312305 MiniUPnP server] to allow local clients to forward ports using UPnP/NAT-PMP/PCP: |
|||
<nowiki>configure |
|||
set service upnp2 listen-on eth1 |
|||
set service upnp2 nat-pmp enable |
|||
set service upnp2 secure-mode enable |
|||
set service upnp2 wan pppoe0 |
|||
commit |
|||
save |
|||
exit</nowiki> |
|||
=== Hardware offloading === |
|||
To enable as much hardware offloading as possible ("[https://help.ubnt.com/hc/en-us/articles/115006567467-EdgeRouter-Hardware-Offloading-Explained Note: It is currently not possible to enable IPv6 offloading for PPPoE and VLANs simultaneously.]"): |
|||
<nowiki>configure |
|||
set system offload ipv4 forwarding enable |
|||
set system offload ipv4 gre enable |
|||
set system offload ipv4 pppoe enable |
|||
set system offload ipv4 vlan enable |
|||
set system offload ipsec enable |
|||
set system offload ipv6 forwarding enable |
|||
set system offload ipv6 pppoe enable |
|||
set system offload ipv6 vlan disable |
|||
commit |
|||
save |
|||
exit</nowiki> |
|||
= Manual configuration = |
|||
= Assumptions = |
|||
* '''eth0''' is plugged directly into the modem or ONT |
|||
* '''eth1''' will be used for your LAN |
|||
* You're using a Home::1 or similar service with one IPv4 address for WAN. |
|||
* Your internal LAN IPv4 range is 192.168.0.0/24, of which you'll use 100 -> 149 for DHCP. |
|||
* A&A have allocated you 2001:8b0:db8::/48 and your internal LAN IPv6 range is 2001:8b0:db8:1234::/64. You'll need to change these values in the configuration to match your actual setup. |
|||
* You have some familiarity with the EdgeRouter Lite and EdgeOS. |
|||
If you're running an older version of EdgeOS or if you prefer to configure your router manually rather than using the setup wizard, you can also use a configuration like the following. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
Don't just blindly copy & paste this whole configuration! |
|||
Pay attention to the comments (lines starting with #) - they give a basic overview of what each section does. |
Don't just blindly copy & paste this whole configuration! Pay attention to the comments (lines starting with #) - they give a basic overview of what each section does. |
||
You'll need to change the IPv6 addresses in this configuration to match the ones shown for you on the control pages, and add your username and password. |
You'll need to change the IPv6 addresses in this configuration to match the ones shown for you on the control pages, and add your username and password. |
||
| Line 188: | Line 243: | ||
# These offload settings are the best compromise from my personal experience |
# These offload settings are the best compromise from my personal experience |
||
# as PPPoE |
# as PPPoE download speeds are generally low enough on A&A connections to not need hardware acceleration |
||
# If you don't use VLANs internally, you might enable ipv6 pppoe offload and disable ipv6 vlan offload |
# If you don't use VLANs internally, you might enable ipv6 pppoe offload and disable ipv6 vlan offload for better IPv6 download performance |
||
# as you can only have one of those two enabled at once |
# as you can only have one of those two enabled at once |
||
set system offload hwnat disable |
set system offload hwnat disable |
||
| Line 204: | Line 259: | ||
set traffic-control smart-queue wan-qos upload rate 20mbit |
set traffic-control smart-queue wan-qos upload rate 20mbit |
||
set traffic-control smart-queue wan-qos wan-interface pppoe0 |
set traffic-control smart-queue wan-qos wan-interface pppoe0 |
||
= Useful commands = |
|||
To check the PPP log: |
|||
tail -f /var/log/vyatta/ppp_pppoe0.log |
|||
To disconnect/connect PPP manually: |
|||
disconnect interface pppoe0 |
|||
connect interface pppoe0 |
|||
To inspect the ports that have been opened for UPnP/NAT-PMP/PCP (this only works when using the 'upnp2' configuration option rather than the older 'upnp' option which uses a different server): |
|||
show upnp2 rules |
|||
[[Category:3rd Party Routers]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 09:15, 25 February 2018
The Ubiquiti EdgeMAX ERLite-3 (EdgeRouter Lite 3) can be used as a router (with a suitable modem) with A&A's services. The router is based on a dual-core MIPS64 processor and runs a Linux distribution called EdgeOS which uses a configuration system forked from Vyatta with a web-based interface on top.
You'll need
- a PPPoE ADSL or FTTC modem, or a fibre ONT (for FTTP). A&A's supplied modems & routers can be configured into a bridge mode for this.
Basic Automatic Configuration
As of recent firmware versions (at least since v1.9.7-hotfix.4) you can almost achieve a working configuration just by using the Basic Setup wizard in the router's web interface, but there are currently a couple of extra configuration changes you have to do manually to fix IPv6 support.
- Connect a computer to the router, access its web interface and start the Basic Setup wizard. Set the 'Internet connection type' option to PPPoE and give it the PPP username and password of your A&A line. Enable the DHCPv6 PD option (which allows for almost entirely automatic configuration of IPv6) and set the IPv6 prefix length that you have set up for your line on the A&A control pages (if you're not sure, it would normally be /64 by default):
- Configure the rest of the Basic Settings Wizard settings however you like or leave them as the defaults.
- Finish the wizard and reboot. Connect your PPPoE modem to the eth0 port on the router, and your LAN to the eth1 port (to match the conventions used by the setup wizard). You should now have a working IPv4 internet connection.
- The two things that need to be done to fix IPv6 support are enabling the IPv6 option for the PPPoE connection, and setting up a default route to use the PPPoE interface because an IPv6 route doesn't get added by default when the connection is established. To add those settings enter the router's command-line interface either by using the CLI button on the web interface or using SSH and then enter the following commands:
configure set interfaces ethernet eth0 pppoe 0 ipv6 enable set protocols static interface-route6 ::/0 next-hop-interface pppoe0 commit save exit
- You don't need to reboot for the changes to take effect and your PPP session should reconnect and come back up with IPv6 configured and working.
Other configuration options
Enabling a 1500 MTU
To enable 1500 MTU if you know that your modem can support baby jumbo frames:
configure set interfaces ethernet eth0 pppoe 0 mtu 1500 set interfaces ethernet eth0 mtu 1508 delete firewall options mss-clamp commit save exit
Enabling UPnP/NAT-PMP/PCP
UPnP, NAT-PMP & PCP are protocols that allow devices behind your router to automatically forward ports.
This can be useful to allow devices such as games consoles to work more easily, but it does have security implications as it allows programs to open holes in your firewall.
To enable the MiniUPnP server to allow local clients to forward ports using UPnP/NAT-PMP/PCP:
configure set service upnp2 listen-on eth1 set service upnp2 nat-pmp enable set service upnp2 secure-mode enable set service upnp2 wan pppoe0 commit save exit
Hardware offloading
To enable as much hardware offloading as possible ("Note: It is currently not possible to enable IPv6 offloading for PPPoE and VLANs simultaneously."):
configure set system offload ipv4 forwarding enable set system offload ipv4 gre enable set system offload ipv4 pppoe enable set system offload ipv4 vlan enable set system offload ipsec enable set system offload ipv6 forwarding enable set system offload ipv6 pppoe enable set system offload ipv6 vlan disable commit save exit
Manual configuration
If you're running an older version of EdgeOS or if you prefer to configure your router manually rather than using the setup wizard, you can also use a configuration like the following.
Don't just blindly copy & paste this whole configuration! Pay attention to the comments (lines starting with #) - they give a basic overview of what each section does.
You'll need to change the IPv6 addresses in this configuration to match the ones shown for you on the control pages, and add your username and password.
Depending on the modem you are using, you may also need to make the changes listed in the comments for a lower MTU.
# Network interface configuration # eth0 - the WAN interface # You'll need to reduce the MTU to 1500 if you don't have a modem that allows you to use baby jumbos set interfaces ethernet eth0 description 'Ethernet interface for PPPoE' set interfaces ethernet eth0 duplex auto set interfaces ethernet eth0 mtu 1508 set interfaces ethernet eth0 speed auto # eth1 - the LAN interface set interfaces ethernet eth1 description 'Local LAN interface' set interfaces ethernet eth1 address 192.168.0.1/24 set interfaces ethernet eth1 address '2001:8b0:db8:1234::1/64' set interfaces ethernet eth1 duplex auto set interfaces ethernet eth1 ipv6 dup-addr-detect-transmits 1 set interfaces ethernet eth1 speed auto # IPv6 SLAAC configuration - this will hand out IP addresses to your local LAN set interfaces ethernet eth1 ipv6 router-advert cur-hop-limit 64 set interfaces ethernet eth1 ipv6 router-advert link-mtu 0 set interfaces ethernet eth1 ipv6 router-advert managed-flag false set interfaces ethernet eth1 ipv6 router-advert max-interval 600 set interfaces ethernet eth1 ipv6 router-advert name-server '2001:8b0:db8:1234::1' set interfaces ethernet eth1 ipv6 router-advert other-config-flag false set interfaces ethernet eth1 ipv6 router-advert prefix '2001:8b0:db8:1234::/64' autonomous-flag true set interfaces ethernet eth1 ipv6 router-advert prefix '2001:8b0:db8:1234::/64' on-link-flag true set interfaces ethernet eth1 ipv6 router-advert prefix '2001:8b0:db8:1234::/64' valid-lifetime 2592000 set interfaces ethernet eth1 ipv6 router-advert reachable-time 0 set interfaces ethernet eth1 ipv6 router-advert retrans-timer 0 set interfaces ethernet eth1 ipv6 router-advert send-advert true # eth2 is unused! set interfaces ethernet eth2 duplex auto set interfaces ethernet eth2 speed auto set interfaces loopback lo # PPPoE configuration - this is your connection to A&A # You'll need to reduce the MTU to 1492 if you don't have a modem that allows you to use baby jumbos # You'll also need to add your connection username & password on the user-id and password lines set interfaces ethernet eth0 pppoe 0 default-route force set interfaces ethernet eth0 pppoe 0 ipv6 dup-addr-detect-transmits 1 set interfaces ethernet eth0 pppoe 0 ipv6 enable set interfaces ethernet eth0 pppoe 0 mtu 1500 set interfaces ethernet eth0 pppoe 0 name-server auto set interfaces ethernet eth0 pppoe 0 password 'your password here' set interfaces ethernet eth0 pppoe 0 user-id 'your username here' # Add a default route for IPv6 traffic (this lets you access the internet over IPv6!) set protocols static interface-route6 '::/0' next-hop-interface pppoe0 # A few basic firewall settings set firewall all-ping enable set firewall broadcast-ping disable set firewall ipv6-receive-redirects disable set firewall ipv6-src-route disable set firewall ip-src-route disable set firewall log-martians enable set firewall receive-redirects disable set firewall send-redirects enable set firewall source-validation disable set firewall syn-cookies enable # Add some firewall groups that'll be useful for creating firewall rules set firewall group ipv6-network-group LAN-v6 ipv6-network '2001:8b0:db8:1234::/64' set firewall group network-group LAN-v4 network 192.168.0.0/24 # internet_in-v6 is for traffic from the internet to the local LAN set firewall ipv6-name internet_in-v6 default-action reject set firewall ipv6-name internet_in-v6 rule 1 description 'Allow incoming ICMP' set firewall ipv6-name internet_in-v6 rule 1 action accept set firewall ipv6-name internet_in-v6 rule 1 protocol icmp set firewall ipv6-name internet_in-v6 rule 9999 description 'Allow return traffic for established and related connections' set firewall ipv6-name internet_in-v6 rule 9999 action accept set firewall ipv6-name internet_in-v6 rule 9999 state established enable set firewall ipv6-name internet_in-v6 rule 9999 state related enable # local-v6 is for traffic from all sources to the router itself set firewall ipv6-name local-v6 default-action reject set firewall ipv6-name local-v6 rule 1 description 'Allow incoming ICMP' set firewall ipv6-name local-v6 rule 1 action accept set firewall ipv6-name local-v6 rule 1 protocol ipv6-icmp set firewall ipv6-name local-v6 rule 2 description 'Allow connections from the LAN' set firewall ipv6-name local-v6 rule 2 action accept set firewall ipv6-name local-v6 rule 2 source group ipv6-network-group LAN-v6 set firewall ipv6-name local-v6 rule 9999 description 'Allow return traffic for established and related connections' set firewall ipv6-name local-v6 rule 9999 action accept set firewall ipv6-name local-v6 rule 9999 state established enable set firewall ipv6-name local-v6 rule 9999 state related enable # internet_in-v4 is for traffic from the internet to the local LAN set firewall name internet_in-v4 default-action reject set firewall name internet_in-v4 rule 1 description 'Allow incoming ICMP' set firewall name internet_in-v4 rule 1 action accept set firewall name internet_in-v4 rule 1 protocol icmp set firewall name internet_in-v4 rule 9999 description 'Allow return traffic for established and related connections' set firewall name internet_in-v4 rule 9999 action accept set firewall name internet_in-v4 rule 9999 state established enable set firewall name internet_in-v4 rule 9999 state related enable # local-v4 is for traffic from all sources to the router itself set firewall name local-v4 default-action reject set firewall name local-v4 rule 1 description 'Allow incoming ICMP' set firewall name local-v4 rule 1 action accept set firewall name local-v4 rule 1 protocol icmp set firewall name local-v4 rule 2 description 'Allow connections from the LAN' set firewall name local-v4 rule 2 action accept set firewall name local-v4 rule 2 source group network-group LAN-v4 set firewall name local-v4 rule 9999 description 'Allow return traffic for established and related connections' set firewall name local-v4 rule 9999 action accept set firewall name local-v4 rule 9999 state established enable set firewall name local-v4 rule 9999 state related enable # Optionally clamp the TCP MSS size to cope with smaller MTUs # These lines are commented out by default, but you'll need to use them if your modem doesn't support baby jumbos # set firewall options mss-clamp interface-type pppoe # set firewall options mss-clamp mss 1452 # Assign firewall rule sets to network interfaces set interfaces ethernet eth1 firewall local ipv6-name local-v6 set interfaces ethernet eth1 firewall local name local-v4 set interfaces ethernet eth0 pppoe 0 firewall in ipv6-name internet_in-v6 set interfaces ethernet eth0 pppoe 0 firewall in name internet_in-v4 set interfaces ethernet eth0 pppoe 0 firewall local ipv6-name local-v6 set interfaces ethernet eth0 pppoe 0 firewall local name local-v4 # Enable internal DHCP set service dhcp-server disabled false set service dhcp-server hostfile-update disable set service dhcp-server shared-network-name LAN authoritative enable set service dhcp-server shared-network-name LAN subnet 192.168.0.0/24 default-router 192.168.0.1 set service dhcp-server shared-network-name LAN subnet 192.168.0.0/24 dns-server 192.168.0.1 set service dhcp-server shared-network-name LAN subnet 192.168.0.0/24 lease 86400 set service dhcp-server shared-network-name LAN subnet 192.168.0.0/24 start 192.168.0.100 stop 192.168.0.149 set service dhcp-server use-dnsmasq disable # Enable internal DNS set service dns forwarding cache-size 150 set service dns forwarding listen-on eth1 # Limit the web GUI to listening on your LAN only set service gui http-port 80 set service gui https-port 443 set service gui listen-address 192.168.0.1 set service gui older-ciphers enable # Limit the SSH server to listening on your LAN only set service ssh listen-address 192.168.0.1 set service ssh listen-address '2001:8b0:db8:1234::1' # Handle NAT for the internet connection set service nat rule 5999 outbound-interface pppoe0 set service nat rule 5999 source address 192.168.0.0/24 set service nat rule 5999 type masquerade # These offload settings are the best compromise from my personal experience # as PPPoE download speeds are generally low enough on A&A connections to not need hardware acceleration # If you don't use VLANs internally, you might enable ipv6 pppoe offload and disable ipv6 vlan offload for better IPv6 download performance # as you can only have one of those two enabled at once set system offload hwnat disable set system offload ipsec enable set system offload ipv4 forwarding enable set system offload ipv4 pppoe enable set system offload ipv4 vlan enable set system offload ipv6 forwarding enable set system offload ipv6 pppoe disable set system offload ipv6 vlan enable # Set up QoS to keep your internet connection usable when doing lots of traffic # You'll need to adjust the upload rate based on your connection's upload sync rate set traffic-control smart-queue wan-qos upload rate 20mbit set traffic-control smart-queue wan-qos wan-interface pppoe0
Useful commands
To check the PPP log:
tail -f /var/log/vyatta/ppp_pppoe0.log
To disconnect/connect PPP manually:
disconnect interface pppoe0 connect interface pppoe0
To inspect the ports that have been opened for UPnP/NAT-PMP/PCP (this only works when using the 'upnp2' configuration option rather than the older 'upnp' option which uses a different server):
show upnp2 rules