VoIP Power: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
|||
| (14 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
[[Category:VoIP Features]] |
[[Category:VoIP Features]] |
||
[[Category:VoIP]] |
[[Category:VoIP]] |
||
=Overview= |
|||
'''A VoIP service needs power, working internet - if either of these has a problem you may be unable to make calls and unable to call Emergency services. Being aware of this and being prepared for such problems is essential.''' |
|||
'''FTTP in the examples...''' On this page the examples include a FTTP ONT - this is the optical device that is provide on fibre circuits by Openreach/CityFibre. Not all services will have an ONT. FTTC and ADSL may have a modem instead, or the modem may be built in to the router itself. The point is that all devices that are used to make the internet work will need to be connected to a UPS. |
|||
=VoIP Vs Analogue= |
|||
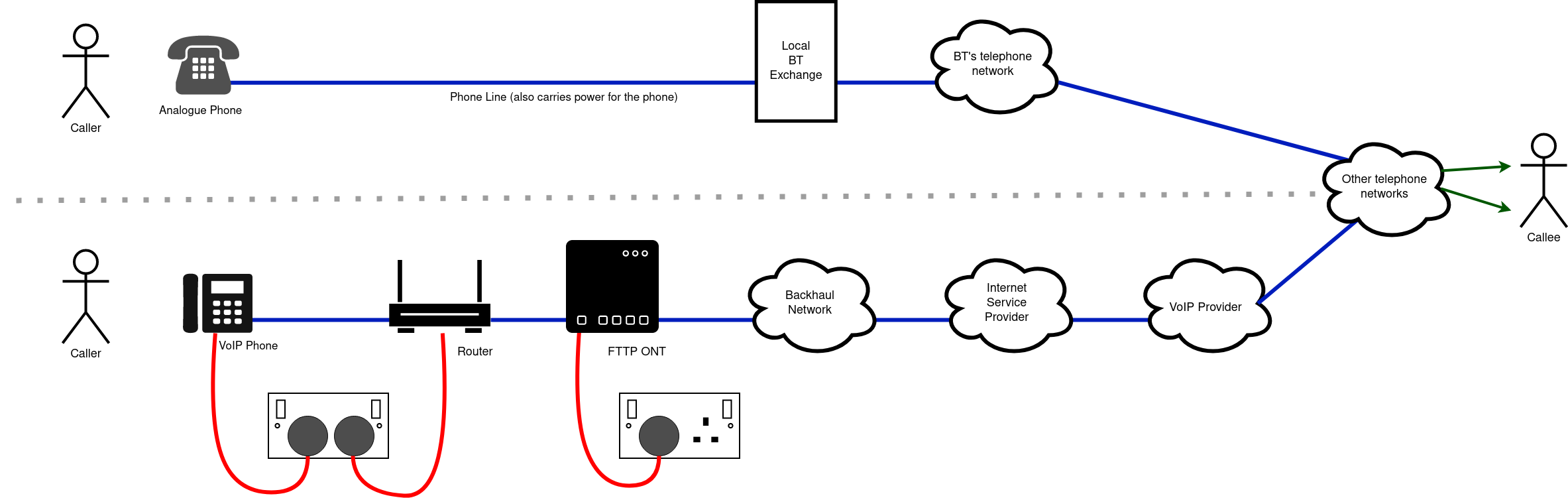
One of the differences between using VoIP for phone calls and using analogue wired phone lines is that that a VoIP service is dependant on a number of other things working, take for example the diagram: |
One of the differences between using VoIP for phone calls and using analogue wired phone lines is that that a VoIP service is dependant on a number of other things working, take for example the diagram: |
||
<div class="res-img"> |
|||
[[File:Analogue-vs-voip.png |
[[File:Analogue-vs-voip.png]] |
||
</div> |
|||
as you can see there is quite a lot |
...as you can see there is quite a lot more involved in making a call over VoIP compared to over the traditional analogue phone: |
||
*VoIP needs local power for the phone |
*VoIP needs local power for the phone |
||
*VoIP needs local power for the router and FTTP ONT |
*VoIP needs local power for the router and FTTP ONT |
||
*VoIP is reliant on the internet connection working |
*VoIP is reliant on the internet connection working |
||
*Internet working also relies on power at the local Street cabinet and/or local exchange or POP |
|||
*Analogue phone doesn't require power |
*Analogue phone doesn't require power |
||
*Analogue phone connects directly via a cable all the way through to the local BT exchange |
*Analogue phone connects directly via a cable all the way through to the local BT exchange |
||
=Considerations= |
|||
As you can see there is a lot more to go wrong. The main things to consider when using VoIP is: |
As you can see there is a lot more to go wrong. The main things to consider when using VoIP is: |
||
* What happens if I lose power |
* What happens if I lose power |
||
* What happens if my internet connection has a fault |
* What happens if my internet connection has a fault |
||
This is especially important to consider when you start to think about access to emergency services. |
|||
==What happens if I lose power== |
|||
Losing power will mean your internet connection goes off and your VoIP phone has no power and no connection to the internet. You'll be unable to make calls. |
|||
===Solutions:=== |
|||
# Use a UPS - an uninterruptible power supply. - typically a heavy box that contains a battery that is kept charged up and will switch to battery power in the event of losing power. |
|||
#Use a mobile phone - Keep a mobile phone close to you and on charge - use this to make phone calls if you lose power. |
|||
'''Test that this works!''' 500VA UPSs from a brand such as APC are available for around £60 which will keep lower power devices such as a router and a phone powered up for a while. |
|||
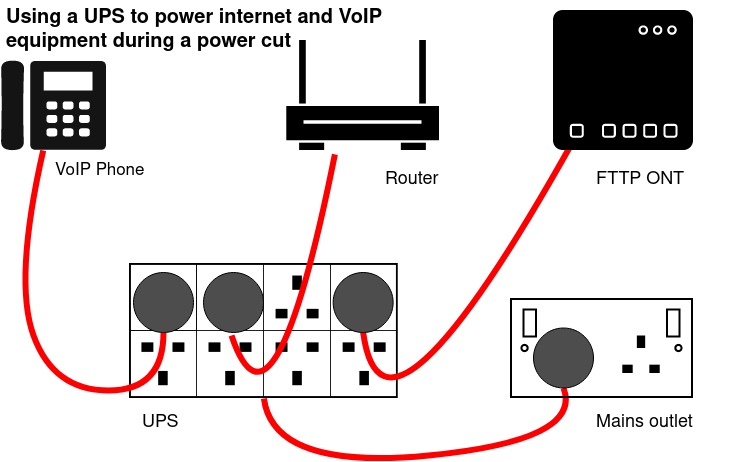
[[File:Ups-connected.png|none|Equipment connected via a UPS]] |
|||
=UPS Suggestions= |
|||
[[File:APC-UPS.png|thumb|an 850VA UPS]] |
|||
*In our tests, to run an FTTC Modem, router and a DECT base station a 400VA UPS will run for about 45 Minutes. |
|||
*To last an hour, we'd suggest a minimum of an 850VA UPS, such as the APC 850VA model pictured here. |
|||
==What happens if my internet connection has a fault== |
|||
A fault on your internet connection will probably affect your VoIP service. You'll be unable to make calls. |
|||
===Solutions:=== |
|||
#'''Use a mobile phone''' - Keep a mobile phone close to you and on charge - use this to make phone calls if you have internet faults. |
|||
# '''Have a backup connection''' Having more than one connection to the internet is important, not just for calling emergency services. A second line, tethering to a mobile, a service that uses a different medium to your main connection (eg satellite) will help keep your internet connection resilient in case of a fault. |
|||
Latest revision as of 11:31, 11 June 2024
Overview
A VoIP service needs power, working internet - if either of these has a problem you may be unable to make calls and unable to call Emergency services. Being aware of this and being prepared for such problems is essential.
FTTP in the examples... On this page the examples include a FTTP ONT - this is the optical device that is provide on fibre circuits by Openreach/CityFibre. Not all services will have an ONT. FTTC and ADSL may have a modem instead, or the modem may be built in to the router itself. The point is that all devices that are used to make the internet work will need to be connected to a UPS.
VoIP Vs Analogue
One of the differences between using VoIP for phone calls and using analogue wired phone lines is that that a VoIP service is dependant on a number of other things working, take for example the diagram:
...as you can see there is quite a lot more involved in making a call over VoIP compared to over the traditional analogue phone:
- VoIP needs local power for the phone
- VoIP needs local power for the router and FTTP ONT
- VoIP is reliant on the internet connection working
- Internet working also relies on power at the local Street cabinet and/or local exchange or POP
- Analogue phone doesn't require power
- Analogue phone connects directly via a cable all the way through to the local BT exchange
Considerations
As you can see there is a lot more to go wrong. The main things to consider when using VoIP is:
- What happens if I lose power
- What happens if my internet connection has a fault
This is especially important to consider when you start to think about access to emergency services.
What happens if I lose power
Losing power will mean your internet connection goes off and your VoIP phone has no power and no connection to the internet. You'll be unable to make calls.
Solutions:
- Use a UPS - an uninterruptible power supply. - typically a heavy box that contains a battery that is kept charged up and will switch to battery power in the event of losing power.
- Use a mobile phone - Keep a mobile phone close to you and on charge - use this to make phone calls if you lose power.
Test that this works! 500VA UPSs from a brand such as APC are available for around £60 which will keep lower power devices such as a router and a phone powered up for a while.
UPS Suggestions

- In our tests, to run an FTTC Modem, router and a DECT base station a 400VA UPS will run for about 45 Minutes.
- To last an hour, we'd suggest a minimum of an 850VA UPS, such as the APC 850VA model pictured here.
What happens if my internet connection has a fault
A fault on your internet connection will probably affect your VoIP service. You'll be unable to make calls.
Solutions:
- Use a mobile phone - Keep a mobile phone close to you and on charge - use this to make phone calls if you have internet faults.
- Have a backup connection Having more than one connection to the internet is important, not just for calling emergency services. A second line, tethering to a mobile, a service that uses a different medium to your main connection (eg satellite) will help keep your internet connection resilient in case of a fault.